2. van Baalen A, Vezzani A, Hausler M, Kluger G. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome: clinical review and hypotheses of epileptogenesis. Neuropediatrics 2017;48:5-18.


3. Lee YJ. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome: refractory status epilepticus and management strategies. Ann Child Neurol 2020;28:8-15.


5. Kramer U, Chi CS, Lin KL, Specchio N, Sahin M, Olson H, et al. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES): pathogenesis, treatment, and outcome: a multicenter study on 77 children. Epilepsia 2011;52:1956-65.


6. Lam SK, Lu WY, Weng WC, Fan PC, Lee WT. The short-term and long-term outcome of febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome in children. Epilepsy Behav 2019;95:117-23.


9. Kanemura H, Sano F, Mizorogi S, Aoyagi K, Sugita K, Aihara M. Duration of recognized fever in febrile seizure predicts later development of epilepsy. Pediatr Int 2012;54:520-3.


11. Sakuma H, Tanuma N, Kuki I, Takahashi Y, Shiomi M, Hayashi M. Intrathecal overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in febrile infection-related refractory status epilepticus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2015;86:820-2.


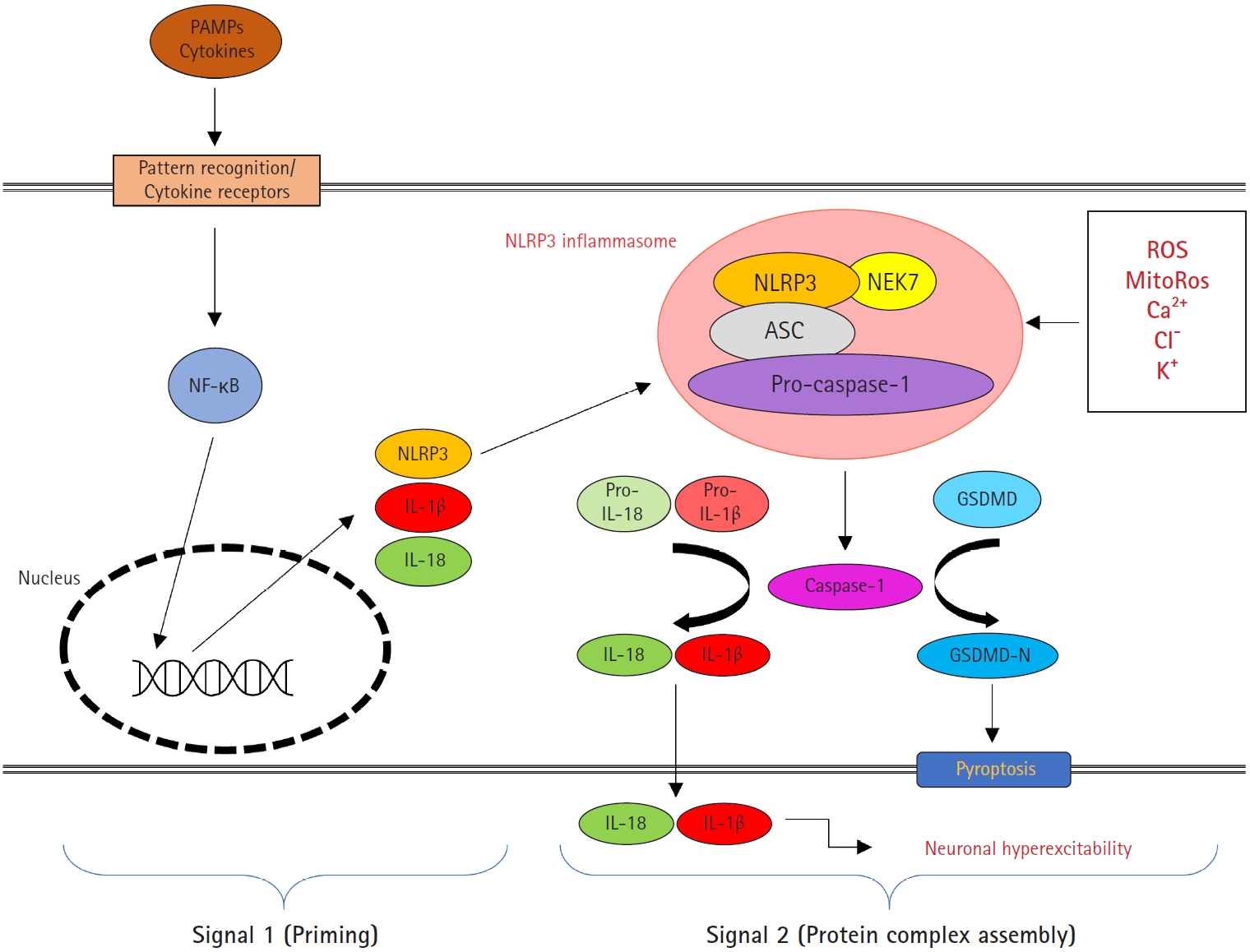
16. Martinon F, Mayor A, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes: guardians of the body. Annu Rev Immunol 2009;27:229-65.


20. Aronica E, Crino PB. Inflammation in epilepsy: clinical observations. Epilepsia 2011;52 Suppl 3:26-32.


21. Ravizza T, Boer K, Redeker S, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Troost D, et al. The IL-1beta system in epilepsy-associated malformations of cortical development. Neurobiol Dis 2006;24:128-43.


22. Ravizza T, Gagliardi B, Noe F, Boer K, Aronica E, Vezzani A. Innate and adaptive immunity during epileptogenesis and spontaneous seizures: evidence from experimental models and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 2008;29:142-60.


23. Roseti C, van Vliet EA, Cifelli P, Ruffolo G, Baayen JC, Di Castro MA, et al. GABAA currents are decreased by IL-1Ī² in epileptogenic tissue of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: implications for ictogenesis. Neurobiol Dis 2015;82:311-20.


25. Akin D, Ravizza T, Maroso M, Carcak N, Eryigit T, Vanzulli I, et al. IL-1Ī² is induced in reactive astrocytes in the somatosensory cortex of rats with genetic absence epilepsy at the onset of spike-and-wave discharges, and contributes to their occurrence. Neurobiol Dis 2011;44:259-69.


26. Kovacs Z, Czurko A, Kekesi KA, Juhasz G. Intracerebroventricularly administered lipopolysaccharide enhances spike-wave discharges in freely moving WAG/Rij rats. Brain Res Bull 2011;85:410-6.


31. Iori V, Iyer AM, Ravizza T, Beltrame L, Paracchini L, Marchini S, et al. Blockade of the IL-1R1/TLR4 pathway mediates disease-modification therapeutic effects in a model of acquired epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 2017;99:12-23.


33. Terrone G, Pauletti A, Pascente R, Vezzani A. Preventing epileptogenesis: a realistic goal? Pharmacol Res 2016;110:96-100.


34. De Simoni MG, Perego C, Ravizza T, Moneta D, Conti M, Marchesi F, et al. Inflammatory cytokines and related genes are induced in the rat hippocampus by limbic status epilepticus. Eur J Neurosci 2000;12:2623-33.


37. Liu Z, Xian H, Ye X, Chen J, Ma Y, Huang W. Increased levels of NLRP3 in children with febrile seizures. Brain Dev 2020;42:336-41.


38. Cristina de Brito Toscano E, Leandro Marciano Vieira E, Boni Rocha Dias B, Vidigal Caliari M, Paula Goncalves A, Varela Giannetti A, et al. NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are up-regulated in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and may contribute to overexpression of caspase-1 and IL-Ī² in sclerotic hippocampi. Brain Res 2021;1752:147230.


39. Saitoh M, Kobayashi K, Ohmori I, Tanaka Y, Tanaka K, Inoue T, et al. Cytokine-related and sodium channel polymorphism as candidate predisposing factors for childhood encephalopathy FIRES/AERRPS. J Neurol Sci 2016;368:272-6.


40. Arend WP. The balance between IL-1 and IL-1Ra in disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2002;13:323-40.


45. Vezzani A, Moneta D, Richichi C, Aliprandi M, Burrows SJ, Ravizza T, et al. Functional role of inflammatory cytokines and antiinflammatory molecules in seizures and epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 2002;43 Suppl 5:30-5.


48. Xu ZH, Wang Y, Tao AF, Yu J, Wang XY, Zu YY, et al. Interleukin-1 receptor is a target for adjunctive control of diazepam-refractory status epilepticus in mice. Neuroscience 2016;328:22-9.


49. Noe FM, Polascheck N, Frigerio F, Bankstahl M, Ravizza T, Marchini S, et al. Pharmacological blockade of IL-1Ī²/IL-1 receptor type 1 axis during epileptogenesis provides neuroprotection in two rat models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 2013;59:183-93.


50. Librizzi L, Noe F, Vezzani A, de Curtis M, Ravizza T. Seizure-induced brain-borne inflammation sustains seizure recurrence and blood-brain barrier damage. Ann Neurol 2012;72:82-90.


55. Heida JG, Teskey GC, Pittman QJ. Febrile convulsions induced by the combination of lipopolysaccharide and low-dose kainic acid enhance seizure susceptibility, not epileptogenesis, in rats. Epilepsia 2005;46:1898-905.


56. Rizzi M, Perego C, Aliprandi M, Richichi C, Ravizza T, Colella D, et al. Glia activation and cytokine increase in rat hippocampus by kainic acid-induced status epilepticus during postnatal development. Neurobiol Dis 2003;14:494-503.


57. Haut SR, Veliskova J, Moshe SL. Susceptibility of immature and adult brains to seizure effects. Lancet Neurol 2004;3:608-17.


60. Sa M, Singh R, Pujar S, DāArco F, Desai N, Eltze C, et al. Centromedian thalamic nuclei deep brain stimulation and Anakinra treatment for FIRES: two different outcomes. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2019;23:749-54.


61. Westbrook C, Subramaniam T, Seagren RM, Tarula E, Co D, Furstenberg-Knauff M, et al. Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome treated successfully with Anakinra in a 21-year-old woman. WMJ 2019;118:135-9.


63. Yang JH, Nataraj S, Sattar S. Successful treatment of pediatric FIRES with anakinra. Pediatr Neurol 2021;114:60-1.


69. Giancane G, Papa R, Vastert S, Bagnasco F, Swart JF, Quartier P, et al. Anakinra in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: long-term safety from the Pharmachild Registry. J Rheumatol 2022;49:398-407.


70. Nabbout R, Mazzuca M, Hubert P, Peudennier S, Allaire C, Flurin V, et al. Efficacy of ketogenic diet in severe refractory status epilepticus initiating fever induced refractory epileptic encephalopathy in school age children (FIRES). Epilepsia 2010;51:2033-7.


73. Bough KJ, Wetherington J, Hassel B, Pare JF, Gawryluk JW, Greene JG, et al. Mitochondrial biogenesis in the anticonvulsant mechanism of the ketogenic diet. Ann Neurol 2006;60:223-35.


74. Dai SS, Zhou YG. Adenosine 2A receptor: a crucial neuromodulator with bidirectional effect in neuroinflammation and brain injury. Rev Neurosci 2011;22:231-9.