 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Child Neurol > Volume 31(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to establish the medical evidence of abuse by comparing the clinical differences between children with shaken baby syndrome (SBS) who had no signs of trauma and traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Methods
Children aged <5 years with intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) were divided into SBS group and TBI group, which was developed because of intentional or accidental trauma including physical violence. We investigated clinical characteristics, ICH and brain injury patterns, funduscopic examinations, and the legal consequences for guardians.
Results
Compared to TBI, children with SBS had a higher incidence of neurological symptoms, including seizures (80.0% vs. 15.4%, P=0.001) and mental changes (73.3% vs. 32.5%, P=0.003); they also had a longer time to hospitalization (SBS, 21.8┬▒30.4 hours; TBI, 9.5┬▒21.3 hours; P=0.046). The rate of bilateral ICH was significantly higher in the SBS group (73.3% vs. 19.0%, P=0.001). In the TBI group, the incidence of epidural hemorrhage (EDH) and subdural hemorrhage was equal (42.3%), but EDH was not seen in the SBS group. Multistage ICH (58.3%) and diffusion-limiting lesions (75.0%) were common in SBS, with high mortality and neurological sequelae (86.7%). Nevertheless, only a few guardians (13.3%) were separated from the victim and only one person (6.7%) who confessed to abuse was detained.
Conclusion
Children with SBS who have never been affected to external physical forces can have multistage and bilateral ICH with severe brain damage, which is clinically different from TBI. Our data suggest that adequate protection and active legal actions are required in order to protect children who had sufficient characteristics of SBS.
Shaken baby syndrome (SBS), first described by Ludwig and Warman in 1984, is characterized by subdural hemorrhage (SDH), retinal hemorrhage (RH), and encephalopathy with minimal or no apparent signs of external trauma to the head and neck [1]. Currently, SBS is often referred to as abusive head trauma (AHT), a term adopted in 2009 because abusive head injuries at up to 5 years of age have several potential causes, including shaking and/or abrupt impact [2]. Accordingly, AHT has two subtypes: (1) brain injury caused by forcibly shaking an infant or toddler (SBS) and (2) injuries caused by hitting the infantŌĆÖs head with a blunt or hard object (intentional injuries). In both cases, the potential for child abuse should be considered, and legal action should be taken if warranted.
Although AHT is relatively easy to diagnose based on other inflicted injuries (such as fractures or bruises) or confession by the perpetrator and/or witnesses to the abusive event [3], intracranial injuries caused by shaking alone usually lack other obvious signs of trauma. Supporting a mechanism for intracranial injuries other than abuse is challenging without a witness or a confession. Consequently, the use of the SBS triad (SDH, RH, and axonal damage or cerebral edema) as meaningful direct evidence of abuse rather than circumstantial evidence remains debatable.
According to Korean legal judgments, children who exhibit the SBS triad are considered victims of abuse even without a witness or a confession [4]. However, Elinder et al. [5] argued that it is reasonable to diagnose a patient with SBS even without clear evidence of the triad, and several other studies have supported this claim [6-10]. Hoskote et al. [6] investigated the association between non-accidental head injury in children with acute SDH and five risk factors: (1) RH; (2) age <12 weeks; (3) inconsistent history; (4) positive skeletal survey; and (5) unexplained bruising. The presence of one of these factors was associated with an 82% probability of non-accidental head injury, two factors with a probability of 93%, and three or more factors with a 100% probability. Notably, bilateral RH, which is common in children with AHT, has an incidence of 1% to 3% in adults, even in those who sustain a severe head injury, suggesting that RH rarely occurs due to accidental external force [7]. In the diagnosis of AHT in children, RH reportedly has a specificity of 93.2%, and severe RH has a 100% specificity [8]. In other words, of the SBS triad, the co-occurrence of SDH with RH suggests a high likelihood of abuse. AHT also accounts for 95% of all serious intracranial injuries and 64% of all head injuries in children [9]. Additionally, the presence of severe neurological symptoms along with SDH and RH is strongly suggestive of AHT in the child [10].
In children with AHT (which is frequently accompanied by other injuries, such as skin bruises or skeletal fractures), prosecution is relatively straightforward. However, in cases of SBS, little evidence of such external damage exists, so legal consequences are often not imposed. Unfortunately, although the reported incidence of child abuse has been steadily increasing, several countries including Korea, Australia, and New Zealand tend not to consider an SBS diagnosis as direct evidence and are lenient regarding criminal charges [11,12]. In Korea, no cases of SBS, even when clinically obvious, have resulted in conviction without a confession or a witness. In contrast, in the United States, numerous convictions have occurred if the victim met the criteria for the SBS triad even with no witnesses or confession [13,14]. Similar legal judgments have also been reported in Japan, the United Kingdom, and Germany [15,16].
The accurate diagnosis of SBS is important because overdiagnosing abuse carries the risk of inappropriate separation from the caregiver, whereas overlooking abuse may expose the victim to repeated violence. Therefore, child abuse in the form of SBS must be diagnosed at an early stage to ensure active legal remediation and minimize recurrence. This study was intended to compare the clinical characteristics of patients with SBS with those of patients with intentional and accidental injuries in Korea, potentially serving as the basis for SBS-related legal judgments.
We collected the medical records of patients diagnosed with intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) between 2011 and 2021 from two tertiary hospitals that provided major medical care in Jeonbuk Province, Korea. In this retrospective investigation, we classified ICH in children into two groupsŌĆöan accidental or intentional injuries group and a shaking groupŌĆöas reported previously [17]. We classified injuries due to accidents or intentional physical violence as traumatic brain injury (TBI). Classification as TBI required at least one of the following: (1) a definite history of a traumatic injury, such as a traffic accident, battery, or fall; (2) accompanying distinct head injuries, such as a skull fracture, cephalhematoma, or facial bruising; (3) a history of traumatic injury compatible with the patientŌĆÖs developmental level; and (4) a confession by the guardian to abuse caused not by shaking, but by assault. SBS was defined as the combination of one or more of subdural hematoma, RH, and axonal injury or cerebral edema [18,19]. Among all patients with ICH, those without external signs of head trauma were included in the SBS group when an individual witnessed or confessed to a shaking event or when the signs were consistent with the SBS triad.
Patients with ICH due to medical or vascular problems were excluded from this study. Medical problems included spontaneous hemorrhage (arteriovenous aneurysm, coagulopathy), cerebral hemorrhage secondary to bacterial meningitis, or injuries during labor (Fig. 1). Even if abuse was suspected, patients who did not meet the SBS triad because of a lack of examination or of witnesses/confession were excluded from the study. The patient history relied on the diagnosis made by the physician responsible for the childŌĆÖs examination at each hospital and/or that recorded in the discharge summary.
The Institutional Review Board of Jeonbuk National University Hospital approved the study protocol (IRB 2022-01-042). Informed consent was waived by the board. Strict patient confidentiality was maintained in the handling of all medical data. Medical records of the eligible patients were retrospectively analyzed to extract the relevant data, including demographic (age and sex) and hospital variables (results of brain computed tomography [CT], brain magnetic resonance imaging [MRI], electroencephalography, skull X-rays, and retinal examination; clinical symptoms such as seizure, vomiting, or mental change; and prognosis). We also examined the legal results in cases of child abuse and separation from the caregivers via consultation with the social welfare team of the hospital.
Descriptive statistics were used to calculate the differences between the definite SBS and TBI groups. We used the mean and standard deviation for continuous data, and frequency and percentage for categorical data. The unpaired t-test was used to compare numerical variables, whereas quantitative variablesŌĆösuch as the number of patients corresponding to each reported symptom, radiologic findings, mode of trauma, and clinical neurologic statusŌĆöwere compared between the groups using Pearson chi-square analysis. P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. All analyses were performed using SPSS version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) for Windows.
A total of 174 children less than 5 years of age diagnosed with ICH were screened for inclusion in this study, of which 32 patients with hemorrhage were excluded due to medical conditions (preterm infant, n=20; bacterial meningitis, n=9; arteriovenous malformation, n=2; Reye syndrome, n=1) (Fig. 1). Four patients who showed no clear evidence of trauma but did not meet the SBS criteria were also excluded. Their caregivers did not witness or confess to abuse, two of them did not undergo retinal examination, and two did not exhibit RH. The included patients were classified into the SBS group (n=15 patients who met SBS diagnostic criteria or had shaking confirmed by a confession or witness) and the TBI group (n=123 patients who displayed ICH with evidence of external force).
The mean age of the SBS group was 5.9┬▒3.3 months, and that of the TBI group was 24.9┬▒19.5 months (Table 1). Children with SBS presented mainly with seizures (80.0%), mental change (73.3%), and vomiting (53.3%), whereas those symptoms were significantly less common in patients with TBI (seizure: 15.4%, P=0.001; vomiting: 23.6%, P=0.026; mental change: 32.5%, P=0.003). Skin lacerations and/or bruising were present in 40.7% of patients with TBI and ICH without any neurological symptoms. Guardian-reported falls, slips, or traffic collisions were the main causes of accidents. For six patients with SBS (40%), the caregiver reported that the child was injured by falling or slipping, whereas four patients with SBS (26.7%) were suspected victims of abuse, as the caregiver did not adequately explain the details of the injury. Notably, guardians of the patients with SBS took an average of 21.8┬▒30.4 hours from the reported time of injury to the hospital visit; this was significantly longer than the patients with TBI, who took an average of 9.5┬▒21.3 hours (P=0.046) to visit the hospital. Moreover, at the time of hospital admission, most of the children with SBS displayed altered consciousness (overall, 73.2%; drowsy, 33.3%, stupor, 26.7%, semicoma, 13.3%), whereas 70.7% of children with TBI entered the hospital in an alert state (P=0.006).
In Fig. 2, we compare the brain hemorrhage patterns of patients with TBI and SBS. All patients in the SBS group had an SDH, with 13% having a subarachnoid hemorrhage, whereas 7% sustained an intraventricular hemorrhage. Intracerebral hemorrhage, epidural hemorrhage (EDH), and extracranial hematoma (ECH) were not seen in any patient with SBS. By contrast, the patients with TBI had a 40% to 42% incidence of EDH, SDH, and ECH; the frequencies of EDH and ECH were also significantly higher than those in the SBS group (P=0.001) (Fig. 2). Bilateral cerebral hemorrhage was also significantly more frequent in the SBS group than in the TBI group (SBS, 73.0%; TBI, 19.0%; P=0.001). In contrast, the incidence of bilateral hemorrhage in patients with TBI and SDH was only 28.8%; therefore, bilateral hemorrhage was significantly more common in the SBS group than in the TBI group (P=0.003) (Fig. 2).
Nine (64.3%) of the children with SBS had at least two multistage hemorrhages as shown by brain CT (Table 2). These findings were confirmed via brain MRI (Table 2 and Fig. 2). Of the 12 children who underwent brain MRI, nine (75%) exhibited diffusion restriction images, and seven (58.3%) had multiple injuries shown on diffusion-weighted images (Fig. 2).
Fig. 3 shows the results of brain MRI and fundus examination in one patient whose guardian was prosecuted. This patient displayed all features commonly observed in the SBS group, such as multistage/bilateral hemorrhages, multiple areas of parenchymal damage on diffusion-weighted images, and RH. As bruises were found on the patientŌĆÖs leg and the guardian confessed, this perpetrator was sentenced to prison and was isolated from the child.
Only one guardian of the children in the SBS group confessed to shaking the child at the time of hospital admission (Table 3). The remaining caregivers said they did not know, mentioned that the patient fell or slipped, or could not accurately explain the cause of symptoms. However, the described traumatic events were incompatible with the developmental level of the patients and no signs of that trauma were observed, except for a bruise on the leg of one patient (Table 1). Police investigations later revealed 10 of the patients to have been abused. Three of those patients did not undergo retinal examinations, but because the shaking was confirmed during the inquiry, they could have been diagnosed with SBS (Table 3).
All of the children had at least one symptom of neurological disturbance, including seizure (80.0%), vomiting (53.3%), mental change (73.3%), or lethargy (33.3%); all but one patient exhibited two or more symptoms. Electroencephalography was performed on 10 patients, all of whom displayed brain dysfunction; some had electrographic status epilepticus or focal seizures. Only two (13.3%) patients with SBS exhibited normal development at follow-up; two patients died (13.3%), and the remaining 11 (73.4%) had developmental disabilities or sequelae of epilepsy. However, only the guardian (6.7%) of the patient with bruising received legal punishment for child abuse, and two patients (13.3%) were temporarily isolated.
AHT, including SBS, is a major cause of serious neurological sequelae in infants and young children [20,21]. SBS is estimated to affect between 1200 and 1600 children per year in the United States [22]. Children diagnosed with SBS have a mortality rate of 15%-30%, with a 50%-70% rate of ongoing neurologic injury [23,24]. Moreover, school-aged victims of SBS exhibit poor neurological outcomes that can result in significant deficiencies in intelligence, working memory, and mental organization [25]. In the present study, the mortality rate was 13.3% and the morbidity rate was 73.3%, which were comparable to previous studies (Table 3). One patient died after discharge, presumably from a recurrence of SBS without any legal safeguard. A report described that 46% of children with a diagnosis of SBS were exposed to abuse before the diagnosis [26]. As such, children diagnosed with SBS have a high probability of previous or future exposure to abuse. Therefore, the recurrence of SBS should be suppressed through early diagnosis and appropriate legal action.
These results sharply contrast with data on patients with a simple traumatic ICH, 50% to 60% of whom recover without neurologic sequelae [27]. The mechanism of injury of SBS is repeated rapid and strong shaking, which causes the brain to strike the skull and tear blood vessels, resulting in bleeding and hematoma [28]. Bleeding can press the brain and cause additional brain damage, whereas shaking injures the nerve axons, resulting in diffuse axonal injury even in the absence of a skull fracture [29]. Regarding the pathophysiology of RH, the theory that vitreous retinal traction is the major factor is the most accepted explanation [30]. Of course, infants may develop RH due to various causes other than shaking, such as increased intracranial pressure, trauma at birth, bacterial meningitis, etc. [6]. However, ocular hemorrhage induced by non-shaking causes tends to disappear completely in 1 week and is usually not accompanied by neurological symptoms [31]. Thus, several authors agree that the presence of the SBS triad in previously healthy children suggests abusive and recurrent trauma [30,32].
Differences between children with TBI and those with SBS observed in this study also substantially corroborate previous findings. We found that axonal injury leads to different clinical symptoms in children with TBI and SBS. Although the frequency of cerebral hemorrhage requiring surgical intervention was similar between the groups, an overwhelming difference was noted in the neurological symptoms, such as mental change, seizures, and vomiting (Table 1). Although the incidence of TBI-associated hemorrhage, such as EDH, SDH, and ECH, was comparable to that in the SBS group (Table 2 and Fig. 2) [33], the probability of bilateral hemorrhage in cases of SDH from TBI was only 28.8%, which is much lower than the proportion of bilateral hemorrhage in children with SBS with SDH (73.3%) (Fig. 3). This difference underscores the importance of observing caution in very young children with SDH, especially bilateral hemorrhage. In addition, bilateral brain hemorrhage or two or more hemorrhagic stages that cannot be explained by one trauma event offer stronger evidence of abuse (Table 2).
With the recent outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019, parenting stress among new parents has increased substantially because of sociodemographic changes and reduced marital satisfaction [34]. The incidence of domestic violence and child abuse has also increased after the pandemic, a social problem that warrants an active response from the authorities [35]. Unfortunately, a key problem in this region, especially in South Korea, is that parents of children with SBS have not been properly prosecuted even when the circumstances of abuse were obvious. This has led to recurrent abuse (Table 3). The only example of sentencing for SBS in Korea was in 2017, in a case in which the victim with the SBS triad died; the court did not admit a relationship between the shaking and death despite video evidence of the perpetrator vigorously shaking the stroller several times [36]. The perpetrator was sentenced to only 3 years and 6 months in prison. In contrast, in the United States, a total of 1431 AHT/SBS criminal convictions were reported from 2008 to 2018; of those, 97% were affirmed/upheld [13].
In the present study, one patient who exhibited the SBS triad (patient 4) was discharged without isolation from his guardian. Two weeks later, he died from sudden respiratory distress while being transported to the hospital. We believe that it is difficult to punish the perpetrators of children with SBS because preventing unnecessary isolation from innocent parents is an important concern, balanced against the importance of protecting children from further abuse. However, the characteristics of SBS are the same regardless of whether the perpetrator confessed, as previously observed [37]. If the SBS triad alone is considered insufficient as legal evidence, it can be interpreted favorably for the perpetrator in the absence of witnesses or a confession. Most cases resulted in an acquittal, which can make parents avoid consequences and increase the risk of recurrence. To counteract this, a social education system regarding child abuse is required to increase the safety of children with SBS after discharge even when the caregiver has been acquitted in court [38].
We recommend that children with suspected SBS always undergo brain MRI, which can confirm bleeding that is not visible on CT scans. This makes it easier to identify additional hemorrhagic stages and bilateral occurrence. Additionally, it is possible to diagnose parenchymal damage on brain MRI that cannot be visualized on brain CT (Table 2 and Fig. 3). Understanding the characteristics of stage 2 or higher bilateral bleeding or parenchymal injury on brain MRI may help add scientific evidence to the diagnosis of child abuse [39], and strengthen the legal basis [40].
In conclusion, children with SBS had a higher incidence of neurological symptoms, including seizures and mental changes, and had a longer time to hospitalization than the TBI group. EDH was not observed in the SBS group; however, the proportion of bilateral ICH was significantly higher. Multistage ICH (58.3%) and diffusion-limiting lesions were common in cases of SBS. Therefore, early retinal examinations are recommended in the case of these characteristic findings, especially in children under 5 years of age. An abuse-specific investigation must be carried out for every child for whom underlying disease has been excluded and who exhibits the appropriate findings for the SBS triad, with no other specific causes.
We also found that even in medically obvious cases of SBS, the childŌĆÖs clinical symptoms were not accepted as direct evidence of abuse in domestic legal judgments. The only caregiver who was successfully prosecuted was sentenced to prison for witnessed abuse and multiple bruising on the lower extremities, not for SBS evidence. Despite the high mortality rate and neurologic sequelae (86.7%) in the SBS group, few guardians (13.3%) were even temporarily separated from the victim, and only one person, who confessed to abuse, was detained.
Our study also highlights the need for awareness regarding the SBS diagnosis, which is essential to protect children from recurring child abuse in Korea. Beyond awareness, however, the study was intended to help prevent abuse by presenting cases based on medical evidence.
Notes
Author contribution
Conceptualization: SJK. Data curation: SYP, MJH, and JHH. Formal analysis: SYP and MJH. Investigation: SYP, MJH, and JHH. Methodology: SYP, MJH, and SJK. Project administration: SYP, MJH, and SJK. Supervision: SJK. Validation: MJH and SJK. Visualization: SYP and MJH. Writing-original draft: SYP and MJH. Writing-review & editing: SYP, MJH, and SJK.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Classification of shaken baby syndrome (SBS) and traumatic brain injury (TBI). ICH, intracranial hemorrhage; RH, retinal hemorrhage; CH, cranial hemorrhage.
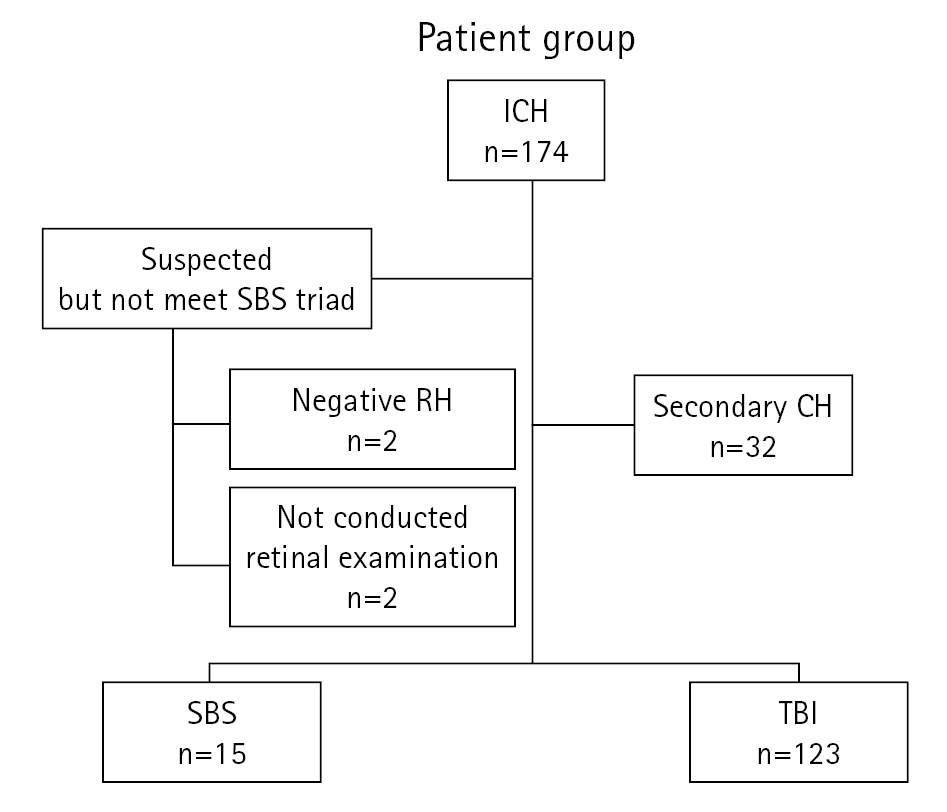
Fig.┬Ā2.
Differences in the hemorrhagic pattern in children with shaken baby syndrome (SBS) versus those with traumatic brain injury (TBI). SDH, subdural hemorrhage; SAH, subarachnoid hemorrhage; ICH, intracranial hemorrhage; EDH, epidural hemorrhage; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; ECH, extracranial hematoma.
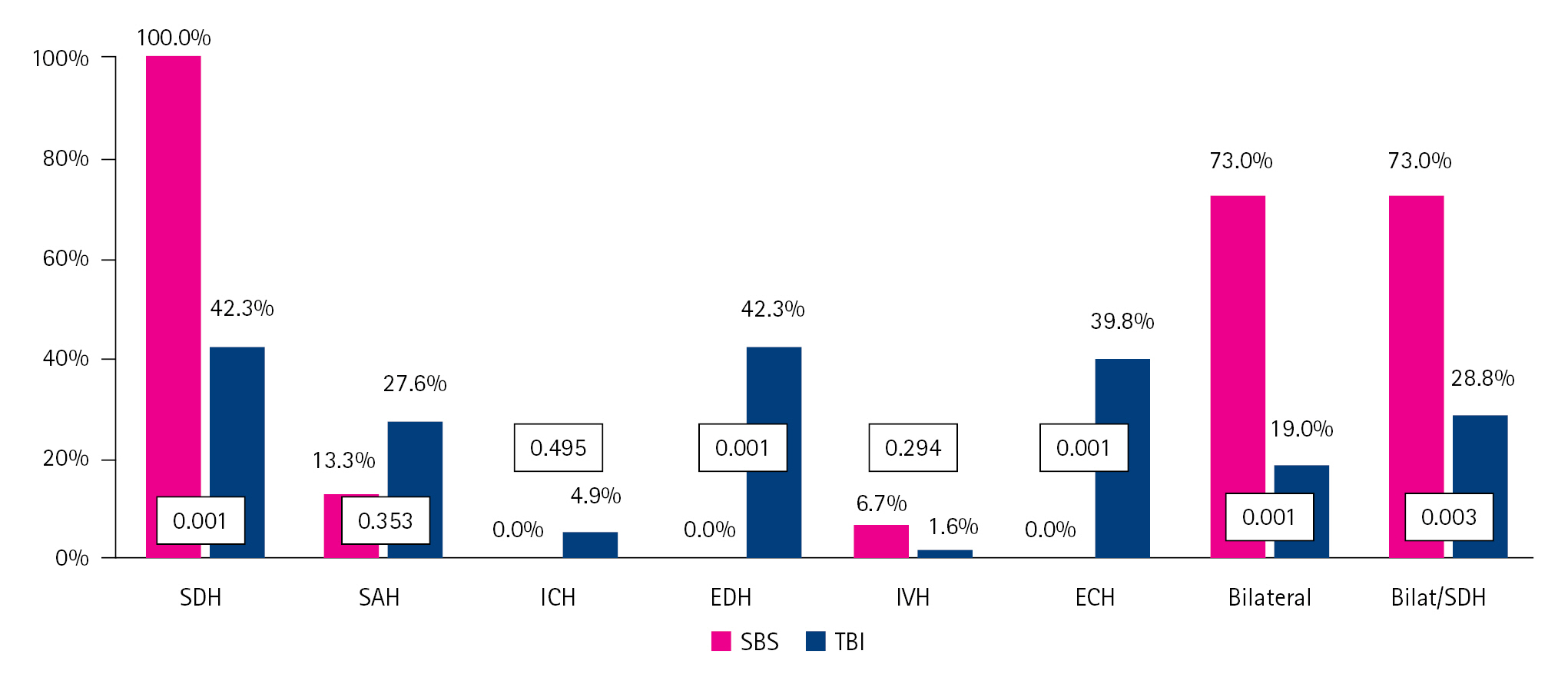
Fig.┬Ā3.
Typical imaging findings of a patient with shaken baby syndrome (SBS). The figure is the result of the only SBS patient whose abuse was accepted in the court and whose guardian was punished. The patient met all of the SBS triads with bruising on the leg. Fundus photograph presented multiple retinal hemorrhage in left eye (A). In addition, bilateral intracerebral hemorrhage occurring at different times (B, C), and multiple cerebral parenchymal damage (D, E, F), which were common findings among SBS children in this study, were seen. The guardian confessed to the shaking event and was the only one who was punished.
Table┬Ā1.
Comparison of patients with traumatic brain injuries and inflicted injuries
| Variable | SBS (n=15, 10.9%) | TBI (n=123, 89.1%) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mo) | 5.9┬▒3.3 | 24.9┬▒19.5 | 0.001a |
| Sex | |||
| ŌĆāMale | 11 (73.3) | 78 (63.4) | 0.573 |
| ŌĆāFemale | 4 (26.7) | 45 (36.6) | |
| Clinical symptoms | |||
| ŌĆāSeizure | 12 (80.0) | 19 (15.4) | 0.001a |
| ŌĆāVomiting | 8 (53.3) | 29 (23.6) | 0.026a |
| ŌĆāIrritability or headache | 1 (6.7) | 38 (30.9) | 0.067 |
| ŌĆāMental change | 11 (73.3) | 40 (32.5) | 0.003a |
| ŌĆāLethargy | 5 (33.3) | 31 (25.2) | 0.538 |
| ŌĆāLaceration/Bruising | 1 (7.1) | 50 (40.7) | 0.014a |
| Trauma mechanism | 0.001a | ||
| ŌĆāAbuse | 4 (26.7) | 1 (0.8) | |
| ŌĆāFall | 3 (20.0) | 61 (49.6) | |
| ŌĆāSlip | 3 (20.0) | 19 (15.4) | |
| ŌĆāOut-of-vehicle TA | 0 | 15 (12.2) | |
| ŌĆāIn-vehicle TA | 0 | 18 (14.6) | |
| ŌĆāUnknown | 3 (20.0) | 0 | |
| ŌĆāOther | 2 (13.3) | 10 (8.1) | |
| Time to hospital visit (hr) | 21.8┬▒30.4 | 9.5┬▒21.3 | 0.046a |
| Mental status | |||
| ŌĆāAlert | 4 (26.7) | 87 (70.7) | 0.006a |
| ŌĆāDrowsy | 5 (33.3) | 17 (13.8) | |
| ŌĆāStupor | 4 (26.7) | 11 (8.9) | |
| ŌĆāSemicoma | 2 (13.3) | 4 (3.3) | |
| ŌĆāComa | 0 | 4 (3.3) | |
| Required operation | 2 (13.3) | 13 (10.6) | 0.668 |
Table┬Ā2.
Computed tomographic and magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with shaken baby syndrome
Table┬Ā3.
Description of clinical findings and prognosis in 15 cases of shaken baby syndrome
| Factor | Pt 1 | Pt 2 | Pt 3 | Pt 4a | Pt 5 | Pt 6 | Pt 7 | Pt 8 | Pt 9 | Pt 10 | Pt 11 | Pt 12 | Pt 13 | Pt 14 | Pt 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mo) | 10 | 1 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 10 | 4 |
| Sex | M | F | M | M | M | M | F | M | M | M | M | F | M | M | F |
| History | |||||||||||||||
| ŌĆāSlip | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| ŌĆāFall | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| ŌĆāShaken | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| ŌĆāUnknown | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| ŌĆāOther | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Time to hospital visit (hr) | 3 | 0.5 | 72 | 21 | 48 | 4 | X | 1 | 24 | 96 | 7 | 48 | 2 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Chief complaint | |||||||||||||||
| ŌĆāSeizure | - | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| ŌĆāVomiting | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| ŌĆāMental change | - | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| ŌĆāLethargy | + | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Retinal hemorrhage | + | + | + | + | + | + | X | + | + | + | + | + | + | X | X |
| EEG | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| ŌĆāAbnormality | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| ŌĆāCPS | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | |||||
| ŌĆāStatus | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | |||||
| Confession or witness | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + |
| Medical prognosis | |||||||||||||||
| ŌĆāNormal | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ŌĆāDevelopmental delay | + | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - |
| ŌĆāEpilepsy | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | - |
| ŌĆāExpired | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| Legal penalty | |||||||||||||||
| ŌĆāNot guilty | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| ŌĆāIsolation | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ŌĆāRemand | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
References
2. Narang SK, Fingarson A, Lukefahr J; Council on Child Abuse and Neglect. Abusive head trauma in infants and children. Pediatrics 2020;145:e20200203.



4. Jeon BJ. Analysis of precedents related to child abuse cases in child care centers applied to the act on punishment against child abuses and its implications. J Korea Contents Assoc 2022;22:538-46.
5. Elinder G, Eriksson A, Hallberg B, Lynoe N, Sundgren PM, Rosen M, et al. Traumatic shaking: the role of the triad in medical investigations of suspected traumatic shaking. Acta Paediatr 2018;107(Suppl 472):3-23.




6. Hoskote A, Richards P, Anslow P, McShane T. Subdural haematoma and non-accidental head injury in children. Childs Nerv Syst 2002;18:311-7.



7. Betz P, Puschel K, Miltner E, Lignitz E, Eisenmenger W. Morphometrical analysis of retinal hemorrhages in the shaken baby syndrome. Forensic Sci Int 1996;78:71-80.


8. Vinchon M, Defoort-Dhellemmes S, Desurmont M, Dhellemmes P. Accidental and nonaccidental head injuries in infants: a prospective study. J Neurosurg 2005;102(4 Suppl):380-4.


9. Billmire ME, Myers PA. Serious head injury in infants: accident or abuse? Pediatrics 1985;75:340-2.



10. Maiese A, Iannaccone F, Scatena A, Del Fante Z, Oliva A, Frati P, et al. Pediatric abusive head trauma: a systematic review. Diagnostics (Basel) 2021;11:734.



11. Statistics Korea. Quality of life indicators in Korea 2020 [Internet]. Daejeon: Statistics Korea; 2020 [cited 2022 Aug 4]. Available from: http://sri.kostat.go.kr
12. Friedman J, Reed P, Sharplin P, Kelly P. Primary prevention of pediatric abusive head trauma: a cost audit and cost-utility analysis. Child Abuse Negl 2012;36:760-70.


13. Narang SK, Sachdev KK, Bertocci K, Pierre-Wright MJ, Kaczor K, Bertocci G, et al. Overturned abusive head trauma and shaken baby syndrome convictions in the United States: prevalence, legal basis, and medical evidence. Child Abuse Negl 2021;122:105380.


14. Tuerkheimer D. The next innocence project: shaken baby syndrome and the criminal courts. Wash Univ Law Rev 2009;87:1-58.
15. Feld K, Feld D, Karger B, Helmus J, Schwimmer-Okike N, Pfeiffer H, et al. Abusive head trauma in court: a multi-center study on criminal proceedings in Germany. Int J Legal Med 2021;135:235-44.




16. Dyer C. Diagnosis of ŌĆ£shaken baby syndromeŌĆØ still valid, appeal court rules. BMJ 2005;331:253.



17. Bechtel K, Stoessel K, Leventhal JM, Ogle E, Teague B, Lavietes S, et al. Characteristics that distinguish accidental from abusive injury in hospitalized young children with head trauma. Pediatrics 2004;114:165-8.



18. Maguire S, Pickerd N, Farewell D, Mann M, Tempest V, Kemp AM. Which clinical features distinguish inflicted from non-inflicted brain injury?: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child 2009;94:860-7.


19. Reece RM, Sege R. Childhood head injuries: accidental or inflicted? Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000;154:11-5.

20. Laurent-Vannier A, Toure H, Vieux E, Brugel DG, Chevignard M. Long-term outcome of the shaken baby syndrome and medicolegal consequences: a case report. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 2009;52:436-47.


21. Barlow KM, Thomson E, Johnson D, Minns RA. Late neurologic and cognitive sequelae of inflicted traumatic brain injury in infancy. Pediatrics 2005;116:e174-85.



22. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Child maltreatment: Fact sheet (2005) Retrieved January 31, 2006 [Internet]. Atlanta: CDC; 2006 [cited 2022 Aug 4]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov
23. Barlow KM, Minns RA. Annual incidence of shaken impact syndrome in young children. Lancet 2000;356:1571-2.


24. Haviland J, Russell RI. Outcome after severe non-accidental head injury. Arch Dis Child 1997;77:504-7.



25. Stipanicic A, Nolin P, Fortin G, Gobeil MF. Comparative study of the cognitive sequelae of school-aged victims of Shaken Baby Syndrome. Child Abuse Negl 2008;32:415-28.


26. Walls C. Shaken baby syndrome education: a role for nurse practitioners working with families of small children. J Pediatr Health Care 2006;20:304-10.


27. Binder H, Majdan M, Leitgeb J, Payr S, Breuer R, Hajdu S, et al. Management and outcome of traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage in 79 infants and children from a single level 1 trauma center. Children (Basel) 2021;8:854.



28. Nadarasa J, Deck C, Meyer F, Willinger R, Raul JS. Update on injury mechanisms in abusive head trauma: shaken baby syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 2014;44 Suppl 4:S565-70.



29. Shannon P, Smith CR, Deck J, Ang LC, Ho M, Becker L. Axonal injury and the neuropathology of shaken baby syndrome. Acta Neuropathol 1998;95:625-31.



30. Clarke MP. Vitreoretinal traction is a major factor in causing the haemorrhagic retinopathy of abusive head injury?: no. Eye (Lond) 2009;23:1761-3.



31. Aryan HE, Ghosheh FR, Jandial R, Levy ML. Retinal hemorrhage and pediatric brain injury: etiology and review of the literature. J Clin Neurosci 2005;12:624-31.


33. Peeters S, Blaine C, Vycheth I, Nang S, Vuthy D, Park KB. Epidemiology of traumatic brain injuries at a major government hospital in Cambodia. World Neurosurg 2017;97:580-9.


34. Taubman-Ben-Ari O, Ben-Yaakov O, Chasson M. Parenting stress among new parents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Child Abuse Negl 2021;117:105080.



35. Sidpra J, Abomeli D, Hameed B, Baker J, Mankad K. Rise in the incidence of abusive head trauma during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Dis Child 2021;106:e14.


36. Suwon District Court. Sentencing 2016 Gohap664 Judgment [Internet]. Seoul: Court of Korea; 2017 [cited 2022 Aug 4]. Available from: https://www.scourt.go.kr/portal/dcboard/DcNewsViewAction.work?bub_name=¤tPage=&searchWord=&searchOption=&gubun=44&seqnum=18738&cbub_code=000250
37. Adamsbaum C, Grabar S, Mejean N, Rey-Salmon C. Abusive head trauma: judicial admissions highlight violent and repetitive shaking. Pediatrics 2010;126:546-55.



38. Diderich HM, Pannebakker FD, Dechesne M, Buitendijk SE, Oudesluys-Murphy AM. Support and monitoring of families after child abuse detection based on parental characteristics at the emergency department. Child Care Health Dev 2015;41:194-202.


- TOOLS







